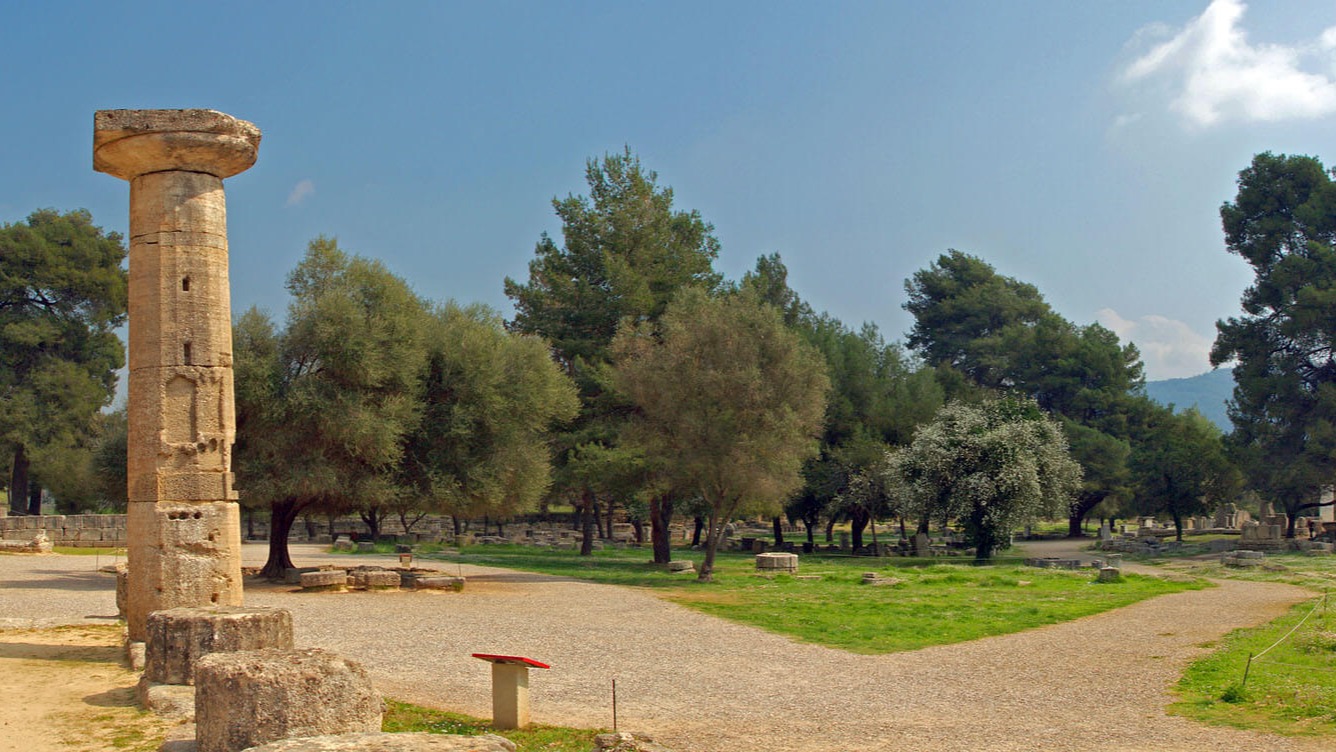
Olympia was the most glorious sanctuary of ancient Greece dedicated to Zeus. It was the venue of the Olympic Games which were held in the context of the Olympics.
Olympia was called Altis, meaning Holy Grove. It was built on the north bank of the river Alfeios. There are traces of human presence from the Neolithic period. Initially it was a rural settlement and gradually evolved into the largest religious center of the ancient world. There was for about a thousand years the ivory statue of Zeus, work of Pheidias, which was known in antiquity as one of the seven wonders of the world. It was 12 m high and consisted of wood inside, but gold, ivory, silver, mountain crystal and semi-precious stones outside. The starting point of the Olympic Games is placed in 776 BC. and was held every four years. However, the Games are already much older, because according to their tradition, Pelopas started, who defeated the king of Pisa Oinomao in a chariot race. The various buildings, of religious and secular character, were gradually erected until the 2nd c. AD the form it has today. The oldest building is the temple of Hera and the newest is Nymphaeum. In Roman times, many buildings were completed and rebuilt as the Romans continued to fight without interruption.
The operation of the sanctuary continued normally during the first Christian years during the reign of Constantine the Great. In 393 AD The last Olympic Games took place and a little later the emperor of Byzantium, Theodosius I, by his decree permanently forbade their performance because they were considered pagan, while during Theodosius II, the final destruction of the sanctuary took place (426 AD).
Remarkable buildings
The most important monuments and buildings of ancient Olympia are:
the Temple of Zeus which was built in the period 470-456 BC and is a model of the Doric style. The sculptures of the Gables are located in the Archaeological Museum of Olympia. Inside the temple was kept the ivory statue of Zeus, which was considered one of the Seven Wonders of the world.
the Temple of Hera or Heraion, where many votive offerings were kept, among which was the famous Hermes of Praxiteles, which is in the archeological museum and the disc of the holy truce which has not been found.
the Bouleuterion, which is located south of the temple of Zeus, outside the sacred precinct of Althea and was the seat of the parliament of Ilia. In front of the statue of the Oath of Zeus, inside the Bouleuterion, "the athletes and the judges took a sacred oath that they would respect the rules of the Games."
the Rectorate, one of the oldest and most important buildings of Olympia, since it was the center of the administrative and political life of the sanctuary and the administrative center of the Olympic Games. Inside the Rectorate the sacred fire burned on the altar of the goddess Hestia.
The entrance to the ancient Stadium
Olympia - the Stadium
the Stadium and its entrance, which was only for officials and athletes. The Olympia Stadium had a capacity of 45,000 spectators. It is 192.27 m long and 28 m wide. On one side it rests on the natural slope of the hill. and on the other hand it has been artificially shaped .. [11] Stands were never built. The spectators were sitting by descent. It was the place where the Olympic Games were held as well as Irea, local celebrations in honor of the goddess Hera.
the Gymnasium, where the athletes' training place was. The gymnasium was topped along its entire length so that athletes could train in road racing regardless of the weather. [11] This was where discus, javelin and running were prepared.
The High School
Palestra, which was part of the Gymnasium, was therefore located outside the sanctuary of Altea on its south side. Here were prepared the fight, the boxing and the pancratium
Leonidas, which was located outside the sanctuary of Althea next to the workshop of Pheidias. It was the place where the officials of the Olympic Games were hosted.
the Workshop of Pheidias, outside the sanctuary of Althea. There Pheidias, the famous Athenian sculptor supervised the construction of the ivory statue of the god Zeus. There was found a cup with the inscription "Pheidium Eimi".
Theikoleon, building west and outside the sanctuary of Althea. It was located north of Pheidias Laboratory and was the seat of the theologians, the priests of Olympia, but at the same time it was the accommodation of all the staff who served permanently in the sanctuary.
Zanes, the bronze statues dedicated to the god Zeus and were located just before the entrance of the Stadium. They were built with money from the fines imposed on illegal athletes.
Philippi, the only circular building in the area of Altea, dedicated to Zeus by Philip II and completed by his son, Alexander the Great.
the Stoa of Echo, which was located inside the sanctuary of Althea, was its eastern boundary and was isolated by the Stadium. It is also known as the Various Stoa due to the paintings that adorned it. Poetry and music competitions took place there.
the Register, a temple dedicated to the mother of the gods, Rea or Kyveli, which was located east of Heraion.
the Southeastern building, a sanctuary probably dedicated to the goddess Estia, which was located in the southeastern corner of Althea and together with the gallery of Echo was the eastern boundary of the sanctuary.
the Altar of Zeus, east of the Temple of Hera has not been saved but there were found numerous bronze figurines in a thick layer of ash.
the Altar of Hera, whose foundations are preserved east of the Temple of Hera and there in modern times the touch of the Olympic Flame that marks the official start of the Winter and Summer Olympic Games. .
In front of the Altar of Hera are the foundations of a prehistoric sanctuary building dating to the Early Helladic III period (2300-2000 BC).
Pelopio, is a mound in the middle of Althea and was dedicated to Pelops, the mythical founder of the Olympic Games.
Kronion Heat or Northern Heat
the Nymphaeum, or the Podium of Herod of Attica, which served as an aqueduct in Roman times, and thanks to it, the water reached the Stadium but also with clay pipes spread throughout the Holy Alta.
the South Stoa, which was built around the same time as the Echo Stoa. It was the southern boundary of the sanctuary and its main entrance from this side.
the House of Nero - East Thermae. A large building complex of the classical era, southeast of Altea and which is attributed to the Roman emperor Nero.
the Greek baths outside the sacred precinct of Altea, near the river Kladeos.
the Hero between Theikoleon and the Greek baths, which was initially associated with the operation of the baths and was later used as a hero.
the Thermes of Leonidas
the Thermes of Kladeou
the Thermi Kroniou
The Treasures were located at the southern foot of Kronion hill, between Nymphaeum and the Stadium. They were treasuries for the preservation of valuable tributes.
the Hippodrome, south of the Stadium, where the chariot races and the equestrian competitions of the Olympic Games took place. Unfortunately he has not been saved.